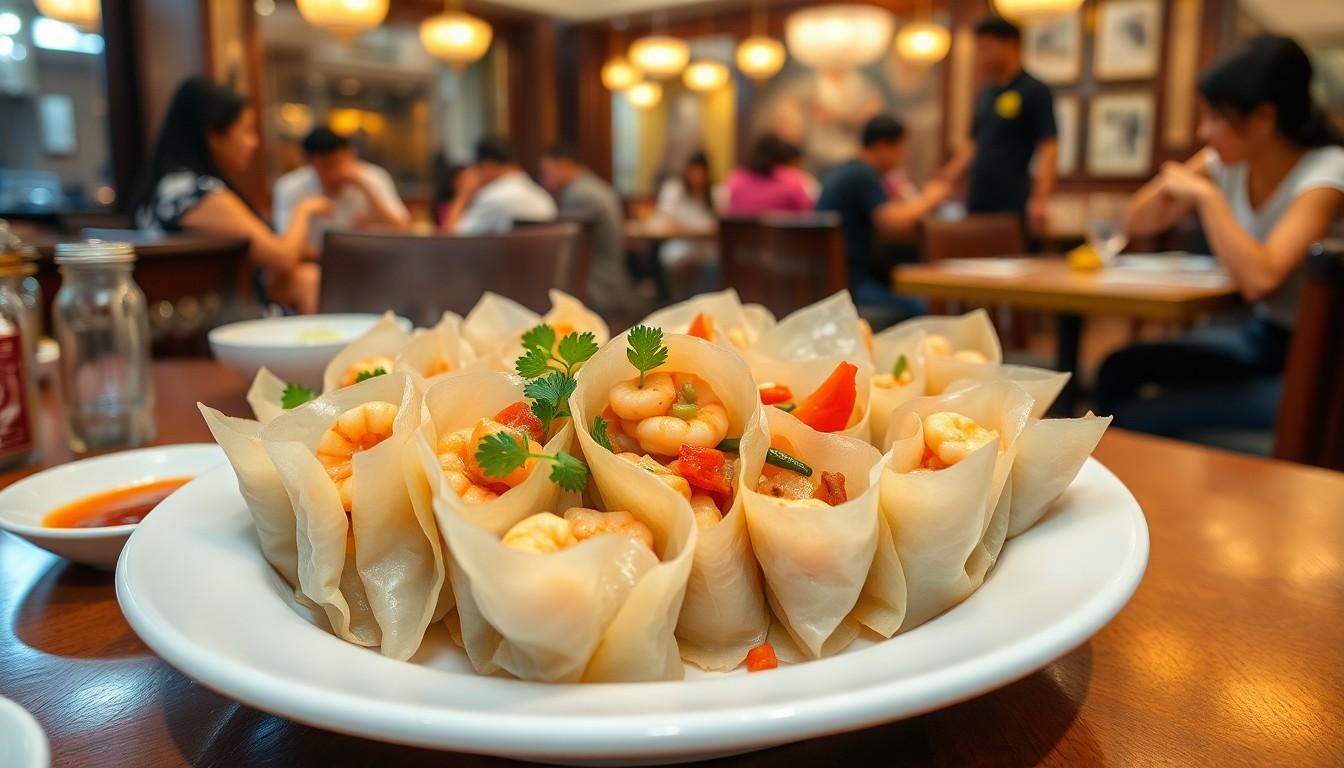
Bikimsum might be the star of your dim sum dreams, but it’s not winning any races in the digestion department. Ever wondered why this delicious treat seems to hang around longer than that friend who overstays their welcome? The answer lies in its unique ingredients and preparation methods that make it both a culinary delight and a digestive challenge.
Packed with rich flavors and often accompanied by a variety of fillings, bikimsum can turn your stomach into a slow cooker. While savoring each bite, it’s important to realize that the very elements that make bikimsum so irresistible are also what contribute to its leisurely exit from your digestive system. So buckle up as we dive into the science behind this delightful dish and uncover why it takes its sweet time to digest.
Understanding Bikimsum
Bikimsum is a beloved dim sum dish celebrated for its diverse flavors and unique fillings. Its composition and the methods used for preparation contribute to its longer digestion time.
What Is Bikimsum?
Bikimsum refers to a style of dim sum often made with a thin dough wrapping and an assortment of fillings. Common fillings include meats, vegetables, and seafood. This dish is typically steamed or fried, enhancing its flavor and texture. The combination of various ingredients provides a rich culinary experience, making it a popular choice in Cantonese cuisine. Diners frequently savor this dish at restaurants or during special occasions, appreciating its intricate preparation.
Nutritional Composition of Bikimsum
Bikimsum contains a blend of macronutrients that influences its digestibility. The dough primarily consists of refined carbohydrates, while fillings introduce proteins and fats. Vegetables add fiber and vitamins, enhancing overall nutrition. These components can complicate digestion, particularly with richer or fatty fillings that slow gastric emptying. Portion sizes often affect the digestion rate as well; larger servings may linger longer in the stomach. Being aware of the nutritional breakdown helps understand why bikimsum might take extra time to digest.
Factors Influencing Digestion

Bikimsum’s digestion can be influenced by various components. Key elements include fiber content and cooking methods.
Fiber Content and Its Role
Fiber plays a significant role in digestion. High fiber content in ingredients such as vegetables affects how quickly the stomach empties. It adds bulk to meals, promoting satiety, which may slow down the overall digestive process. Those filling choices enhance the flavor of bikimsum but can lead to prolonged digestion. Additionally, dietary fiber improves gastrointestinal health. Yet, if consumed in large amounts, it may cause bloating or discomfort, further extending digestion time.
Cooking Methods and Their Impact
The cooking methods used for bikimsum can also slow digestion. Steaming keeps the dish moist, while frying adds fats. Both techniques contribute to a richer texture and flavor. However, fats take longer to break down in the stomach compared to carbohydrates and proteins. Consequently, bikimsum, with its blend of cooking styles, can linger longer in the digestive tract. Cooking temperatures and times affect nutrient availability and digestibility, creating variations in how quickly the body processes bikimsum.
The Digestive Process
The digestive process for bikimsum involves several complex stages. First, the stomach begins breaking down the food as it mixes with gastric juices. Strong acids and enzymes help dissolve fats and proteins, creating a semi-liquid substance called chyme. This mixture needs time to fully break down rich fillings and processed ingredients in bikimsum, which can include multiple types of meat and seafood.
The small intestine plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption. It receives the chyme from the stomach and continues breaking down the components with the help of bile and pancreatic enzymes. Nutrients from bikimsum get absorbed as the food moves through the intestinal tract. However, the thickness of the dough and the variety of fillings can slow this process considerably.
Stomach and Intestinal Breakdown
Bikimsum’s complex composition affects how it breaks down in the stomach and intestines. Different ingredients require different processing times. Starchy elements like dough take time to dissolve, while protein components need additional breakdown. Each ingredient’s unique properties contribute to the overall duration of digestion. Additionally, larger portion sizes can make it even harder for the stomach to handle. This complexity leads to slower gastric emptying, causing bikimsum to linger longer inside.
Timeframe for Digestion
On average, the digestion of bikimsum can take anywhere from three to six hours. This timeframe varies based on several factors, including the specific ingredients and the cooking method used. Heavier fillings, such as minced meat or seafood, contribute to longer digestion times. When combined with a rich dough, these ingredients form a challenging meal for the digestive system. While lighter dishes might digest more quickly, bikimsum’s hearty nature slows this process, leading to extended satiety.
Health Implications
Bikimsum’s digestion time affects both health benefits and potential discomforts. Understanding these can inform choices around this favorite dish.
Benefits of Slow Digestion
Slow digestion often promotes prolonged satiety, helping with weight management. It’s known that the extended feeling of fullness can reduce the desire for snacking between meals. Nutrients are absorbed efficiently over time, enhancing overall nutrient availability. Certain ingredients in bikimsum, like vegetables, contribute fiber, which supports gut health. Slower digestion may also help stabilize blood sugar levels, preventing spikes after meals.
Potential Discomforts
Certain individuals might experience discomfort due to bikimsum’s slow digestion. Bloating can occur, particularly with high-fiber fillings. Feelings of heaviness in the stomach may result from the rich ingredients or larger portion sizes. Digestive issues such as gas may arise with certain combinations of foods. Consuming bikimsum in moderation can mitigate these potential discomforts. Adjusting ingredients can also lead to a more balanced experience without the adverse effects.
Conclusion
Bikimsum’s delightful flavors and textures come with a unique digestive challenge. Its rich ingredients and cooking methods contribute to a longer digestion time. While this slow process can enhance satiety and nutrient absorption, it may also lead to discomfort for some.
Understanding the factors that affect digestion can help diners make informed choices. Enjoying bikimsum in moderation and being mindful of ingredient selections can create a more pleasant dining experience. Ultimately, appreciating the balance between taste and digestion allows enthusiasts to savor this beloved dish without the drawbacks.